Predicting Depression Among University Students: a Comparative Assessment of ML & DL models using XAI
Jun 1, 2024·,,,,,·
0 min read
Jahid Hasan Rony
MM Mahbubul Syeed
Razib Hayat Khan
Kaniz Fatema
Md Shakhawat Hossain
Mohammad Faisal Uddin
Abstract
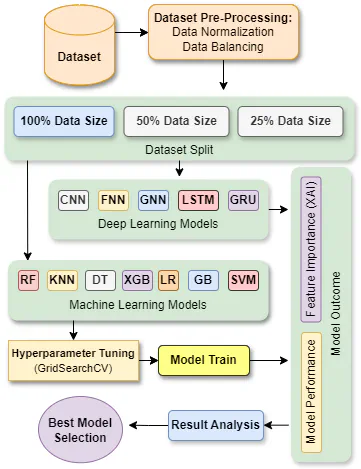
Depression among university students is a critical mental health issue that significantly impacts their academic performance, social interactions, and overall well-being. This study investigates the efficacy of machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) models in measuring depression, a significant global mental health concern. Leveraging depression data (PHQ-9) from a survey conducted in the 15 top-ranked universities, our research aims to contribute to students’ mental health awareness and support systems with cutting-edge technology. A wide range of ML and DL models are evaluated for this task. Performance is assessed using conventional metrics (e.g., accuracy, precision, and recall), as well as using explainable AI (XAI) to measure the feature extraction capabilities of the models in relation to their prediction accuracy across different dataset sizes. It has revealed that DL models focused more on clinically relevant features in the case of measuring depression. Considering feature importance and performance metrics, different models are applicable for different scenarios, however, overall LSTM, CNN, and SVM are the three top-performing models. Additionally, we found that a hybrid approach, using CNN for feature selection followed by SVM for classification helps to improve the overall accuracy from 0.979 to 0.984. By investigating and bench-marking both ML and DL models, this research establishes a comprehensive basis for the development of effective and easy-to-use AI-based depression measurement tools. Therefore, this study contributes to the early detection and prevention of students’ academic depression and supports the well-being of society at large.
Type
Publication
2024 23rd International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies (ISCIT)